Inbound HTTP component
The Inbound HTTP component is able to receive messages through HTTP requests. It will act like a webservice that listens for HTTP requests. Once a message is received, it's content will be handed over to the next component in the flow.
Configuration
The Inbound HTTP component has the following configuration options:
Endpoint
A name to identify this component's endpoint (URL).
The test and production URL to 'reach' this component is shown on the bottom the component configuration.
- It can only contain letters, numbers and these special characters:
@,.,_,+,~,?. - It should contain between 3 and 50 characters.
- It has to be unique (within a tenant)
The maximum body size of a request to an Inbound HTTP component is 10MB.
Protocol
Select which protocol will be used by the web service.
Options
httphttps(default)
Tenant part
Select if the tenant name or ID is used in the URL.
Options
Tenant ID(default)Tenant name
Match prefix?
Whether you want use the URL of the endpoint as a prefix. See One Inbound HTTP multiple URL's for more info.
Options
YesNo(default)
Preserve HTTP headers
Whether you want to keep the Camel HTTP headers on the exchange instead of removing them from the exchange.
Options
YesNo(default)
Exchange pattern
This option determines how the component responds to incoming messages. By default it is set to Request reply, this means it will reply to an incoming request with the result of the flow. Even when a flow's Transport Type is set to asynchronous.
The response that's sent back by the Inbound HTTP component is the body and headers (exchange) at the end of the flow. Alternatively, the response is the body and headers (exchange) before reaching the first component whose 'Exchange pattern' is set to One way.
If the Exchange pattern of the ContentRouter in the example below is set to Request reply the Inbound HTTP component will respond with the state of the exchange at point 2. It will respond with the state of the exchange at point 3, when the ContentRouter is set to One way.
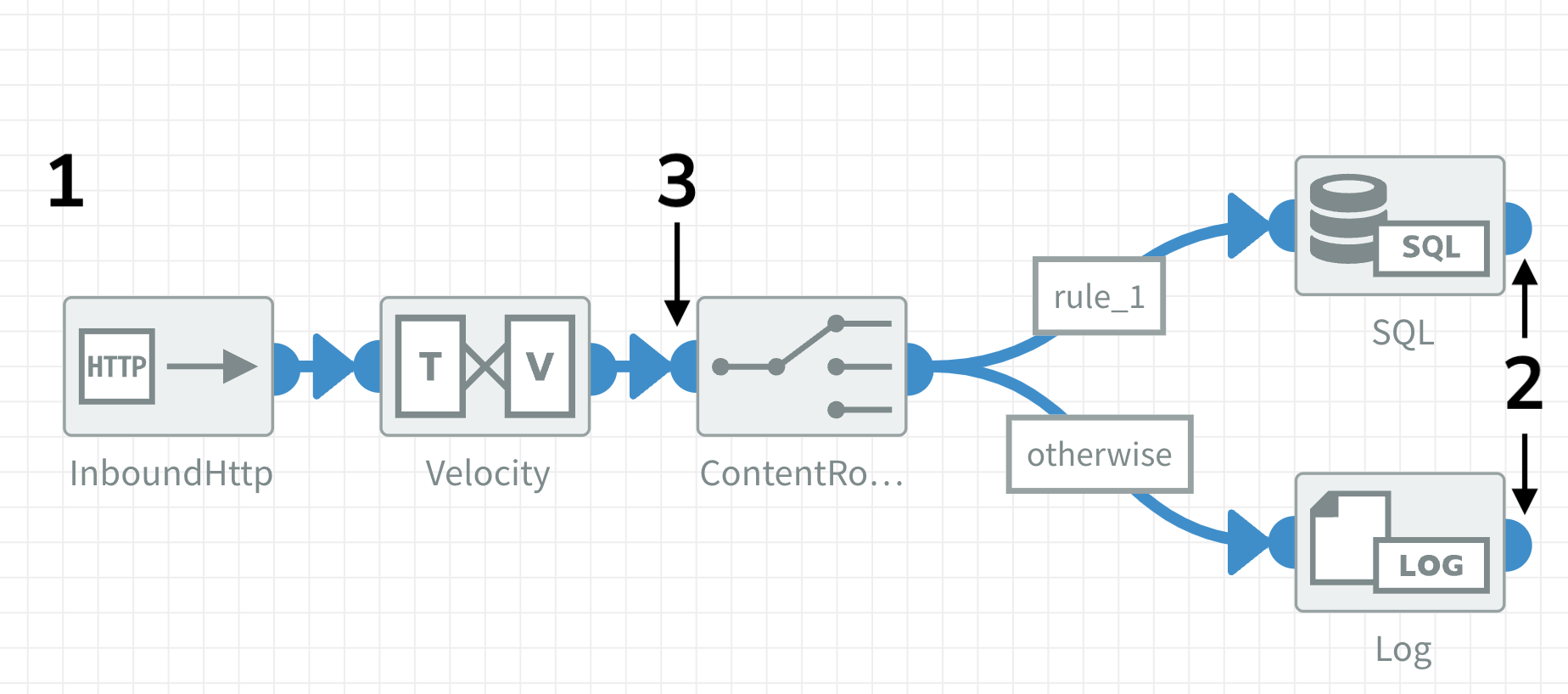
Sometimes you don't need the result of a flow as a response or, depending on the size and complexity of the flow, processing can take too much time for the Inbound HTTP component to send back a result. Some clients like Postman will wait untill they get a response, but other clients or applications might not wait long enough and timeout.
Set the exchange pattern to One way to recieve a response immediately after sending a request to an Inbound HTTP component (point 1 in the image above). It will respond with HTTP code 200 OK and it will return the body it received. This setting works only in flows that have transport type set to asynchronous and queues.
Options
One wayRequest reply(default)
For Request reply the timeout option of a flow may need to be increased to give it some time to process the incoming message(s).
Dovetail might respond to a request with a 500 error. Often this doesn't mean the server isn't up and running, but there are headers in the response that are too big to send back.
Use a RemoveHeaders component before the point where the response is sent back and clean up the headers. In the image above: after the SQL / Log or before the ContentRouter component.
Reaching the webservice
HTTP
An Inbound HTTP with the following settings:
- Endpoint named
dovetail_endpoint_name, - Protocol set to
http, - Tenant part set to
Tenant IDand the tentant ID is 123456
Will have a webservice URL that looks like this:
http://[host name]:[port]/123456/dovetail_endpoint_name
Port is 8000 for Test and 9000 for Production.
HTTPS
An Inbound HTTP with the following settings:
- Endpoint named
dovetail_endpoint_name - Protocol set to
https - Tenant part set to
Tenant nameand the tenant name is dovetail
Will have a webservice URL that looks like this:
https://[host name]/inbound_http/test/dovetail/dovetail_endpoint_name
Old format HTTPS
The old format of the HTTPS URL's is still supported. The URL above will look like this in the old format:
https://[host name]:[port]/dovetail/dovetail_endpoint_name
Port is 8001 for Test and 9001 for Production.
One Inbound HTTP multiple URL's
By default the webservice will only match the exact URL that is specified in the Endpoint property. In the Reaching the webservice examples above it is only possible to reach the webservice by sending messages to the exact .../dovetail_endpoint_name URL.
If you also want to reach the same webservice with .../dovetail_endpoint_name/user and/or .../dovetail_endpoint_name/order you can set Match prefix? to Yes. This way dovetail_endpoint_name is the prefix for your webservice and it can be reached with messages that use different URL's.
You can read the full URL or the partial URI of the inbound request from the CamelHttpUrl or CamelHttpUri header respectively. They are available when the Preserve HTTP Headers option is set to Yes.
Testing the webservice
Use a REST client, like Postman, to send messages to an Inbound HTTP component in Dovetail. This makes it possible to manually trigger or send test data to a flow.
To send messages you will need to:
- Enter the URL of the webservice as described above.
- Set the dropdown to POST.
- When you want to send an XML or JSON body:
- Click on the Body tab and choose message format Raw.
- Paste your XML or JSON in the text area field.
- When you want to send headers along:
- Click on the Headers tab and fill in the Key (header name) and Value.
- Click Send to submit the message.
You can verify wether the message was recieved succesfully in the Flow Manager, under Flow details or Flow Transactions.
You can send a header to a flow with an Inbound HTTP component by adding it as a parameter:
- append
?name=valueto the url to send a header with headernamenameand headervaluevalueto that flow. i.e.https://demo.dovetail.world/test/tenant/endpoint?name=value. - send multiple headers by adding an
&in between?name1=value1&name2=value2.